Difference Between Speed and Velocity
What is velocity?Velocity is defined as the rate of change of displacement.
- It is a vector quantity, both magnitude and direction are required to define it.
- It's direction is same as that of displacement.
- SI unit of velocity is m/s
Speed is defined as the rate of change in distance with respect to time.
- It is a scalar quantity. Only magnitude is required to define the speed.
- Speed and velocity both have same unit.
Now sometimes students ask questions like
Is average speed = average velocity?
The answer is no, average speed is not equal to average velocity. This is becauseAverage Speed = Total distance/Total time
Average Velocity = Total displacement/Total time
Just like both displacement and distance are different, average speed and average velocity are also different for ex. Motion around a circular track.
3. Average velocity
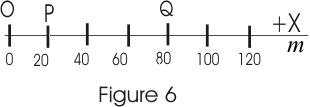
- Consider a particle undergoing motion along a straight line i.e. particle is moving along X-axis.
- Here in this case X co-ordinate describing motion of the particle from origin
O varies with time or we can say that X co-ordinate depends on time. - If at time t=t1 particle is at point P , at a distance x1 from origin and at time t=t2 it is at point Q at a distance x2 from the origin then displacement during this time is a vector from point P to Q and is
Δx=x2−x1 (1)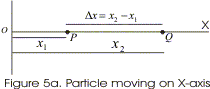
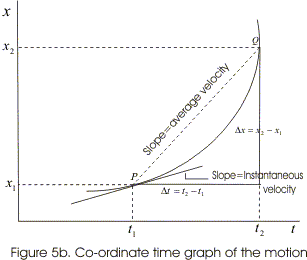
- The average velocity of the particle is defined as the ratio of the displacement Δx of the particle in the time interval Δt=t2-t1. If vavg represents average velocity then,

- Figure (5b) represents the co-ordinate time graph of the motion of the particle i.e., it shows how the value of x-coordinate of moving particle changes with the passage of time.
- In figure (5b) average velocity of the particle is represented by the slope of chord PQ which is equal to the ratio of the displacement Δx occurring in the particular time interval Δt.
- Like displacement average velocity vavg also has magnitude as well as direction i.e.,average velocity is a vector quantity.
- Average velocity of the particle can be positive as well as negative and its positive and negative value depends on the sign of displacement.
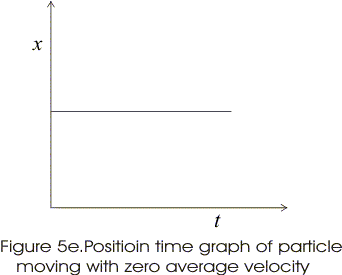
- If displacement of particle is zero its average velocity is also zero.
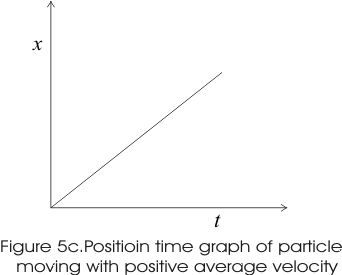
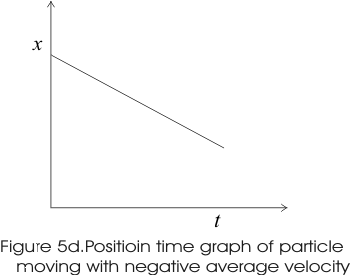
- Graphs below shows the x-t graphs of particle moving with positive, negative average velocity and the particle at rest.
average velocity definition
Average velocity is defined as the ratio of total displacement to total time. It is the average values of the velocities we know.
average velocity formula
This is extra section where we talk about average velocity formula. From average velocity definition we know that it is the ratio between total displacement and total time but this vav i.e., average velocity formula can have different form according to different problems. So before solving problems that asks you to find average velocity please check under which case your problem falls.
- Case 1:-
IfX is total displacement of the body andt is the total time taken by the body to complete the displacement.The average velocityVav is given byvav=Total distance traveledtotal time taken=XT - Case 2:-
If we know that body have initial displacement positionx0 at timet0 undergoes a motion and attains final displacementxf at timetf then, the average velocity is given asvav=xf−x0tf−t0=Δ xΔ t - Case 3:-
If we have a knowledge thatx1,x2,.....xn are the distance covered by the body for timet1,t2,.....tn . The average velocity isx1+x2+.......+xnt1+t2+.......+tn - Case 3:-
If a velocity is changing as a result of a constant acceleration, the average velocity can be found by adding the initial and final velocities, and dividing by 2. Here it is important to note that this formula applies only for constant acceleration case.
Consider a body moving with uniform acceleration along a straight path. At some instant of time, initially its velocity isU m/s and at the end of t seconds let its final velocity beV m/s. Hence the average velocity is given asHow to derive this average velocity formulavav=v+u2
Average velocity is displacement divided by time. Let us start with the formula for displacement and divide it by t.s=ut+12at2averagevelocity=ut+12at2t=u+12at=2u+at2=u+(u+at)2
now,v=u+at averagevelocity=u+v2
Average Speed
- From graph 5c it is clear that for positive average velocity slope of line slants upwards right or we can say that it has positive slope.
- For negative average velocity slope line slants upwards down to the right i.e. it has negative slope.
- For particles at rest slope is zero.
- So far we have learned that Average speed is defined as total distance traveled divided by time taken.
- Displacement of the object is different from the actual distance traveled by the particle.
- For actual distance traveled by the particle its average speed is defined as the total distance traveled by the particle in the time interval during which the motion takes place.
- Mathematically,
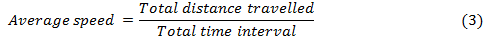
- Since distance traveled by an particle does not involve direction so speed of the particle depending on distance traveled does not involve direction and hence is a scalar quantity and is always positive.
- Magnitude of average speed may differ from average velocity because motion in case of average speed involve distance which may be greater than magnitude of displacement.
- From this we can say that average speed depending on distance is in general greater than magnitude of velocity.
Let us now consider some of the solved examples for the concepts Average speed and Average velocity. Questions are important for understanding the concept. Try to understand these solved examples and then try to solve few questions on your own.
0 comments:
Post a Comment