June 06, 2018
2.Average velocity
- Consider a particle moving along a curved path in x-y plane shown below in the figue
- Suppose at any time,particle is at the point P and after some time 't' is at point Q where points P and Q represents the position of particle at two different points.
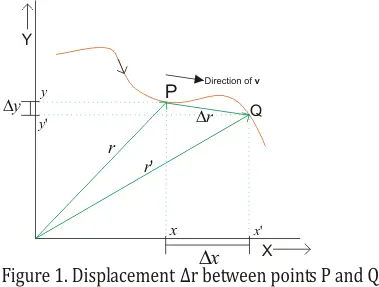
- Position of particle at point P is described by the Position vector r from origin O to P given by
r=xi+yj
where x and y are components of r along x and y axis
- As particle moves from P to Q,its displacement would be would be Δr which is equal to the difference in position vectors r and r'.Thus
Δr = r'-r = (x'i+y'j)-(xi+yj) = (x'-x)i+(y'-y)j = Δxi+Δyj (1)
where Δx=(x'-x) and Δy=(y'-y)
- If Δt is the time interval during which the particle moves from point P to Q along the curved path then average velocity(vavg) of particle is the ratio of displacement and corresponding time interval
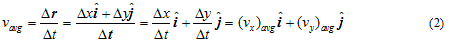
since vavg=Δr/Δt , the direction of average velocity is same as that of Δr
- Magnitude of Δr is always the straight line distance from P to Q regardless of any shape of actual path taken by the particle.
- Hence average velocity of particle from point P to Q in time interval Δt would be same for any path taken by the particle.

0 comments:
Post a Comment