2.Position and Displacement
(a) Position:
- To locate the position in motion or at rest,we need a frame of refrence.
- Simplest way to choose a frame of refrence is to choose three mutually perpendicular axis labelled as X-,Y- and Z- axis as shown in figure below


More about Frame of reference
-
We know that we need a frame of reference is needed to locate the position of any object. For that we choose rectangular co-ordinate system of three mutually perpendicular axis that are
x , y and z axis. The point of intersection of these three axes is called Origin 'O' and is considered as the Reference Point.
The x , y and z co-ordinates describe the position of object with respect to the co-ordinate system. To measure time , we need a clock. The co-ordinate system along with a clock constitutes a Frame of reference. So , the frame of reference is a co-ordinate system , with a clock w.r.t. which, an observer can describe the position, displacement etc. of an object.
Frames of reference are of two types:-
- Inertial frame of reference:- These are the frame of reference in which Newton's first law of motion is applicable.
Non-Inertial frame of reference:- These are the frame of reference in which , Newton's first law of motion is not applicable
- Such system of labeling position of an object is known as rectangular coordinates system
- If A(x,y,z) be the position of any point in rectangular co-ordinates system it can be labeled as follows
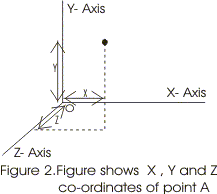
- Point O is the point of intersection of these mutually perpendicular axis and is known as reference point or origin of frame of reference
- To measure a time ,we can also attach a clock with this frame of reference
- If any or all co-ordinates of the object under consideration changes with time in this frame of reference then the object is said to be in a motion w.r.t the frame of the reference otherwise it is at rest
- For describing motion in one dimension we need one set of co-ordinates axis i.e only one of X,Y and Z axis
- Similarly for two and three dimensions we need two or three set of axis respectively
- Motion of an object along a straight line is an example of motion in one dimension
- For such a motion, any one axis say X-axis may be choose so as to coincide with the path along which object is moving
- Position of the object can be measured w.r.t origin O shown in the figure

- Position to the right of the origin has positive values and those to the left of origin O has negative values.
We know that we need a frame of reference is needed to locate the position of any object. For that we choose rectangular co-ordinate system of three mutually perpendicular axis that are x , y and z axis. The point of intersection of these three axes is called Origin 'O' and is considered as the Reference Point.
Thex , y and z co-ordinates describe the position of object with respect to the co-ordinate system. To measure time , we need a clock. The co-ordinate system along with a clock constitutes a Frame of reference. So , the frame of reference is a co-ordinate system , with a clock w.r.t. which, an observer can describe the position, displacement etc. of an object.
Frames of reference are of two types:-
The
Frames of reference are of two types:-
- Inertial frame of reference:- These are the frame of reference in which Newton's first law of motion is applicable. Non-Inertial frame of reference:- These are the frame of reference in which , Newton's first law of motion is not applicable


(b) Distance and displacement:
- In the graph shown below an object is at position P at time t1 and at position R at time t2.
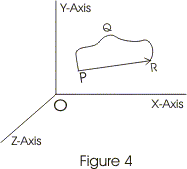
- In the time interval from t1 to t2 particle has traveled path PQR and length of the path PQR is the distance traveled by the object in the time interval t1 to t2
- Now connect the initial position of the object P with its final position R through a straight line and we get the displacement of the object.
- Displacement of the object has both magnitude and direction i.e., displacement is a vector quantity.
- Magnitude of displacement vector is equal to the length of straight line joining initial and final position and its direction points from the initial position of object towards its final position.
- In contrast to displacement distance is scalar quantity.

0 comments:
Post a Comment