5. Acceleration
- Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with time.
- For describing average acceleration we first consider the motion of an object along X-axis.
- Suppose at time t1 object is at point P moving with velocity v1 and at time t2 it is at point Q and has velocity v2. Now average acceleration of object in moving from P to Q is

which is the change in velocity of object with the passage of time. - Instantaneous acceleration can be defined in the same way as instantaneous velocity

- The instantaneous acceleration at any instant is the slope of v-t graph at that instant.
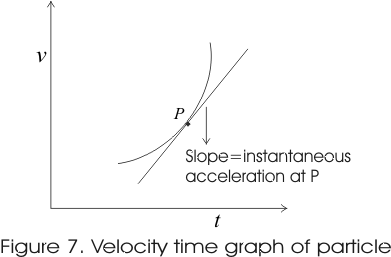
- In figure 7 instantaneous acceleration at point P is equal to the slope of tangent at this point P.
- Since velocity of a moving object has both magnitude and direction likewise acceleration depending on velocity has both magnitude and direction and hence acceleration is a vector quantity.
- Acceleration can also be positive, negative and zero.
- SI unit of acceleration is ms-2
0 comments:
Post a Comment